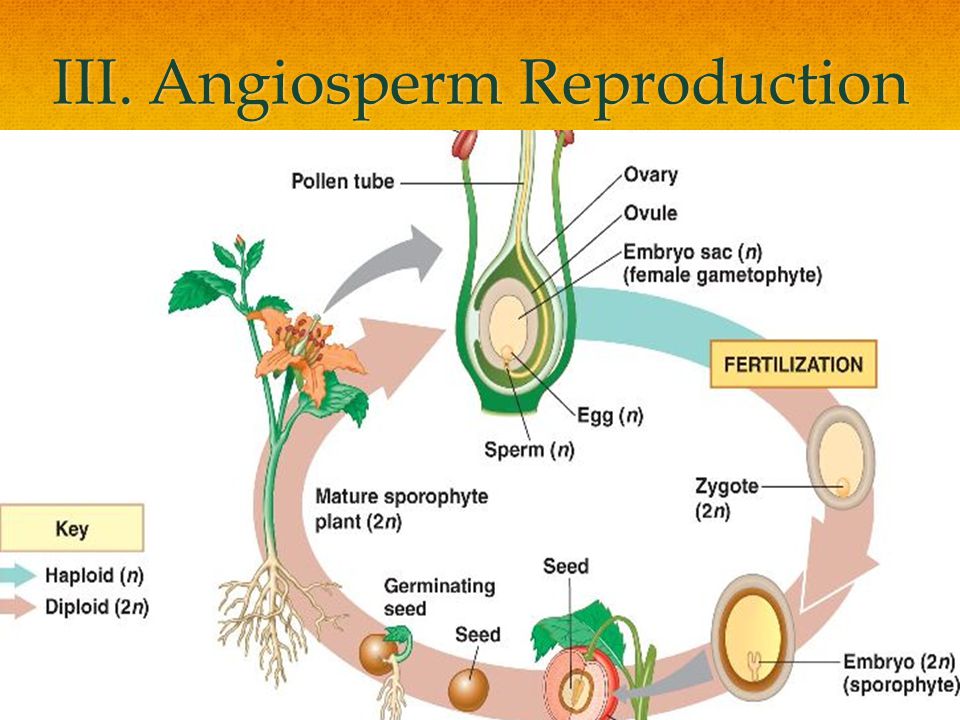
Breeder seed is the initial source of seed and is usually produced by the breeder It is the source for the production of prebasic or basic seed Prebasic seed is the progeny of the breeder seed and is usually produced under the supervision of a breeder or his designated agencyReproduction in angiospermophytes 932 Distinguish between pollination, fertilization and seed dispersal Pollination The process of pollen transfer from an anther to a stigma Fertilization The fusion of a male gamete with a female gamete inside the ovule This forms a zygote Seed and fruit formation After the fertilization, the calyx, corolla, androecium, style and stigma wilt and fall out, only the ovary remains Fruit formation The ovary stores food, increases in size and ripens, transforming into a fruit, due to the hormones (auxins) that are secreted by the ovary, the ovary's wall transforms into the pericarp

Seed Wikipedia
Seed reproduction examples
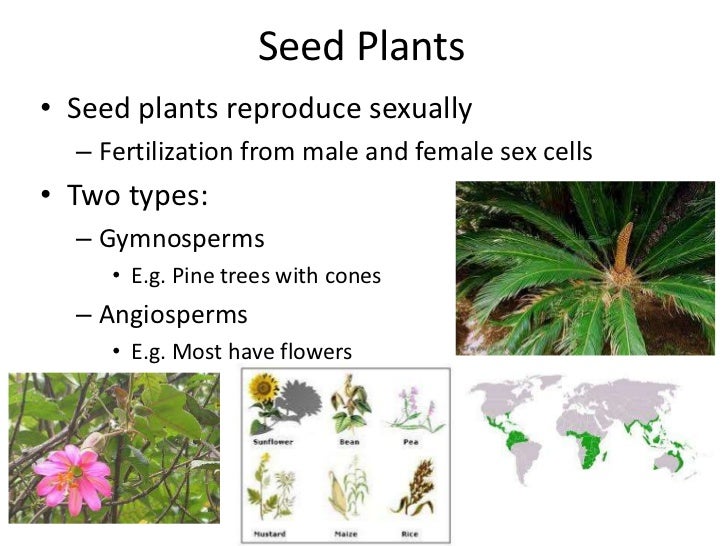
Seed reproduction examples-Definition of Seed A true seed is defined as a fertilized mature ovule that possesses embryonic plant, stored material, and a protective coat or coats Seed is the reproductive structure characteristic of all phanerogams The structure of seeds may be studied in such common types of pea, gram, bean almond or sunflowerThe seed habit is the most complex and evolutionary successful method of sexual reproduction found in vascular plants Today, seed plants, gymnosperms ("Nacktsamer", ca 800 living species) and angiosperms ("Bedecktsamer", flowering plants, ca living species), are by far the most diverse lineage within the vascular plants (see figure below)



Chapter 24 Reproduction Of Seed Plants By Mihael Maldonado
A pollen grain is transferred from one flower to another A pollen tube grows from the stigma to the ovary After fertilisation, the female parts of the flower develop into a fruit the ovulesSeed plants have special structures on them where male and female cells join together through a process called fertilisation After fertilisation, a tiny plant called an embryo is formed inside a seed The seed protects the embryo and stores food for it Sexual reproduction in Moss Moss produce 2 kinds of jacketed gametes — eggs & sperm Egg producing organ is called the archegonium Eggs are larger and nonmotile Sperm producing organ is called the antheridium Sperm are smaller, flagellated cells Antheridia & archegonia are both part of the gametophyte plant
Reproduction by seed is called sexual reproduction It requires pollination and fertilization of an egg which results in seed that is capable of producing a new plant Seed production varies greatly among and within weed species in part due to environmental variability Apomixis (asexual seed formation) is the result of a plant gaining the ability to bypass the most fundamental aspects of sexual reproduction meiosis and fertilization Without the need for male fertilization, the resulting seed germinates a plant that develops as a maternal clone This dramatic shift in reproductive process has been documented in many flowering plant Reproduction is a critical time in plant life history Therefore, genes affecting seed dormancy and germination are among those under strongest selection in natural plant populations Germination terminates seed dispersal and thus influences the location and timing of plant growth After seed shedding, germination can be prevented by a property
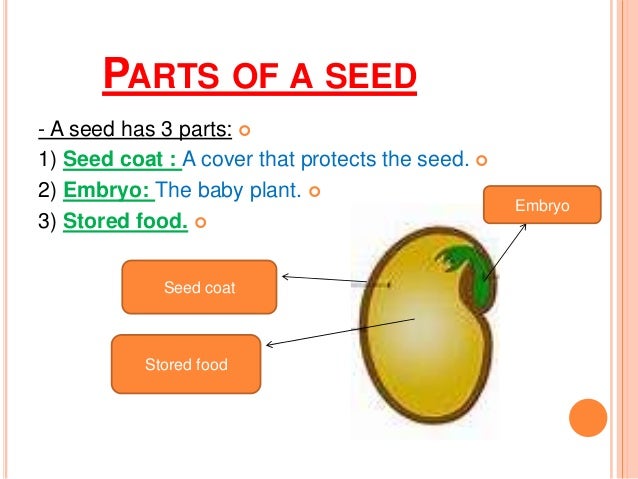
A seed is an embryonic plant enclosed in a protective outer covering The formation of the seed is part of the process of reproduction in seed plants, the spermatophytes, including the gymnosperm and angiosperm plants Seeds are the product of the ripened ovule, after fertilization by pollen and some growth within the mother plantChapter 13 Sex and reproduction in nonseed plants Almost all plants are capable of reproduction without sex Most commonly this happens as a consequence of the plant being severed into pieces and these pieces being able to regenerate the parts that were lost Additionally, some species have developed pieces that are particularly prone to beSeed, the characteristic reproductive body of both angiosperms (flowering plants) and gymnosperms (eg, conifers, cycads, and ginkgos) Essentially, a seed consists of a miniature undeveloped plant (the embryo), which, alone or in the company of stored food for its early development after germination , is surrounded by a protective coat (the testa)




The Importance Of Pollen And Seeds Ppt Video Online Download
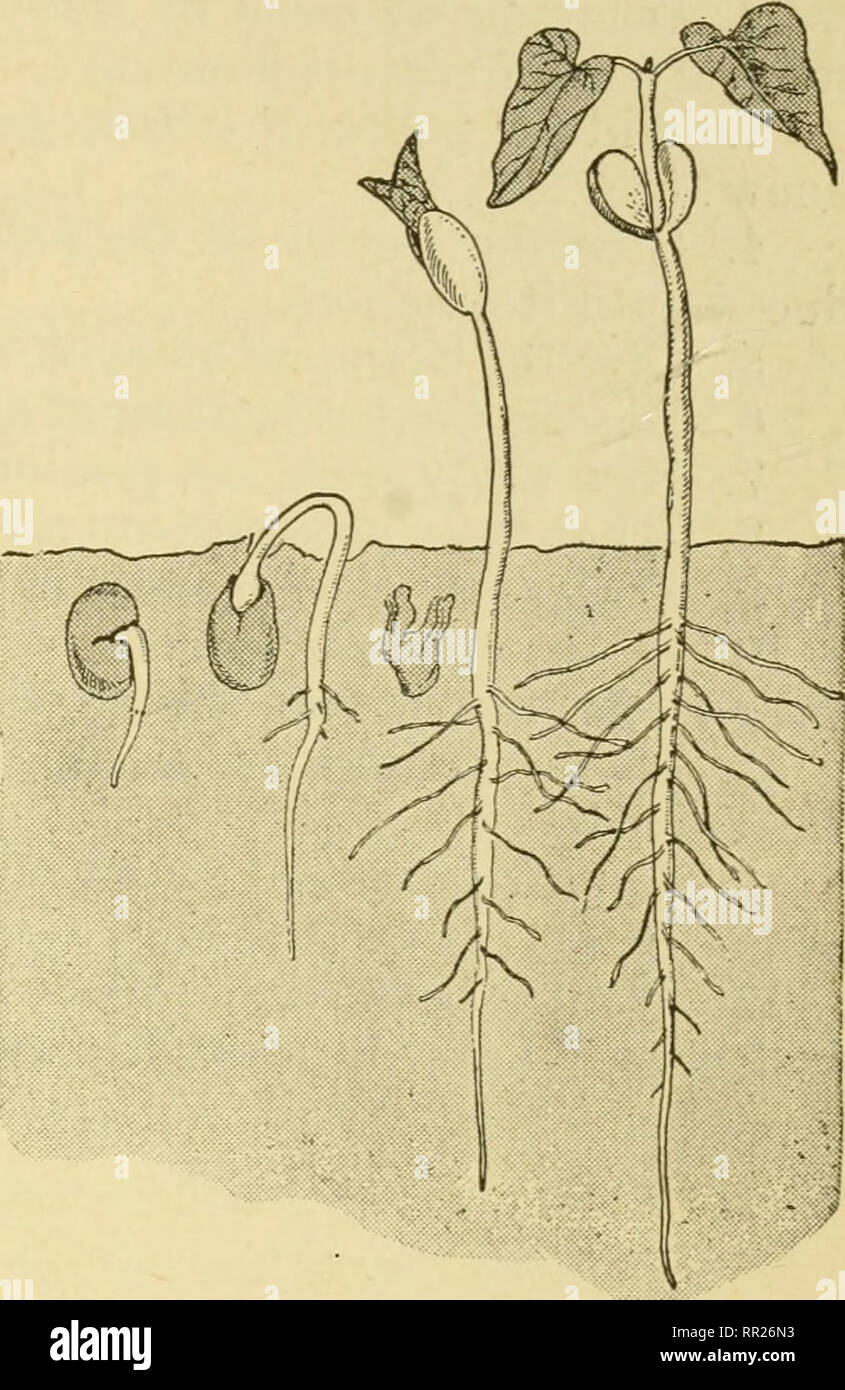



Advanced Biology Biology Physiology Reproduction Formation Of The Seed And Fruit 279 In The Grains The Endosperm Is A Well Developed Localized And Easily Identified Structure In Seeds Such As Beans Peas
Seed production is a form of sexual reproduction, with all the genetic variation that sexual reproduction brings with it, where as vegetative reproduction is asexual andOne way is by being exceptionally good at asexual reproduction One of the oldest living organisms on Earth is a peat moss in Hawaii that has been asexually reproducing since a single spore landed on the islands 50,000 years ago How did a group that relies so heavily on water for reproduction become so successful on land?




Effect Of Pcap2 On Arabidopsis Seed Germination Seedling And Download Scientific Diagram




Ch 30 The Evolution Of Seed Plants Ch 38 Angiosperm Reproduction And Biotechnology Ch 39 Plant Responses To Inte In 21 Biology Units Plant Physiology Ap Biology
(2) the megasporangium, unlike that of heterosporous seedless plants, is covered by one or two cellular layers called integuments and is termed an ovule; Each seed, then, is genetically unique There are several types of asexual reproduction in plants, but all produce the same result genetically identical daughter plants VielleCalzada's quest to develop an asexual seed began a decade ago, when he decided to investigate apomixis, a specific type of asexual reproductionEach spruce tree carries male and female cones The larger female cones contain ovules, which develop into egg cells, or female gametophytes To reproduce, the smaller male cones let



1




Plants Test 2 Review Flowers Seeds Reproduction Diagram Quizlet
Seed plants produce the spores via sexual reproduction They require bees and/or male and female plants to make them bloom and create seeds Seedbearing plants differ from all other plants in that their gametes – or mature cell that requires germination with another male or female mature haploid to grow – do not require water for fertilizationWell, its how a new generation comes into being Flowering plants need to produce seeds in order to be able to make new plantsDiscovering Reproduction There are two ways Narcissus pseudonarcissus can reproduce either by seed or by producing bulbs Different circumstances require either of these different methods of reproduction for this plant First, the wild daffodil can reproduce by generating seeds, which is a sexual method of reproduction




Fern Reproduction Seed Less Vascular Plants Diagram Quizlet



9 3 Reproduction In Angiospermophytes Bioninja
Chapter 15 Sex and Reproduction in Seed Plants Seeds are a remarkable innovation that have been highly important to the evolution of plant life The vast majority of plants that we observe and utilize possess seeds and seed plants dominate most terrestrial habitats The last chapter described, in general terms, what seeds are and what Seed plants have special structures on them where male and female cells join together through a process called fertilisation After fertilisation, a tiny plant called an embryo is formed inside a seed The seed protects the embryo and stores food for it The parent plant disperses or releases the seedHemp Breeding and Seed Production Hemp Breeding and Seed Production is an 3 halfday online course designed to enhance the knowledge of professionals working on hemp improvement and propagation The course covers hemp seed production topics such as flowering, pollination, seed development, harvesting and certification




Seed Kids Britannica Kids Homework Help




Loh Pei Hang D 2 3 Plants Reproduce
4 Main Steps of Hybrid Seed Production Plant Breeding The following points highlight the four main steps of hybrid seed production The steps are 1 Choice and Development of Seed Parent (ALine) 2 Choice and Development of Restorer or Male Parent (RLine) 3 Maintenance and Multiplication of Parental Seeds 4 If the seed germinates, it may grow into a mature sporophyte tree, which repeats the cycle Summary In gymnosperms, the gametophyte generation takes place in a cone, which forms on the mature sporophyte plant Each male gametophyte is just a few cells inside a grain of pollen Each female gametophyte produces an egg inside an ovulePlants produce flowers to make seeds To make a seed a flower must be pollinated Pollen from the male part of one flower travels to the female part of another flower where the seeds are made




Pdf Sexual And Apomictic Seed Reproduction In Aronia Species With Different Ploidy Levels Semantic Scholar




Reproduction Without Seeds By Hanisha Brar On Prezi Next
Once the propagule drops from the parent tree there is an obligate dispersal period which each species' propagule must remain in the water During this period embryonic development continues For the red mangrove this dispersal period is the longest at 40 days The black mangrove's propagule must drift for at least 14 days Mast seeding, the intermittent, synchronous production of large seed crops by a population of plants, is a wellknown example of resource pulses that create lagged responses in successive trophic levels of ecological communities These lags arise because seed predators are thought capable of increasing reproduction and population size only after the resource pulse is(4) the ovule matures as a seed;



Growing Plant Stages Color Line Icon The Seed Germination Growth Reproduction Pollination And Seed Spreading Pictogram For Stock Vector Illustration Of Contour Drawing




Complex Body Of Seed Reproduction Of Flowering Angiosperms Stock Photo Picture And Royalty Free Image Image
Reproduction seed plants Seeds produced by seed plants produced from the process of pollination (pollen fall on white) After that there will be a process of fertilization (conception), this process will evolve so that the resulting embryos will eventually be formed drupe Detailed descriptions please learn the material »Reproduction seed plants Lastly, seed reproduction – but this is extremely rare! Seeds generated by apomixis are a means of asexual reproduction, involving the formation and dispersal of seeds that do not originate from the fertilization of the embryos Hawkweed (Hieracium), dandelion (Taraxacum), some Citrus (Citrus) and Kentucky blue grass (Poa pratensis) all use this form of asexual reproduction




Plant Reproduction Bioninja



How Seep Plants Reproduce Study Sheet Hanford Christian School Jane Kitson
Not every plant grows from a seed Some plants, like ferns and mosses, grow from spores Other plants use asexual vegetative reproduction and grow new plants from rhizomes or tubers We can also use techniques like grafting or take cuttings to make new plants Explore topicsAbout Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us CreatorsSeed Artillery works on many different types of projects and can often deliver results when others cannot The scope of the work done is very wide and is unique to the artillery piece that needs to be restored or repaired We meet NSSA standards on all replica work and hold each project to the highest standards




Ppt Seed Reproduction Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
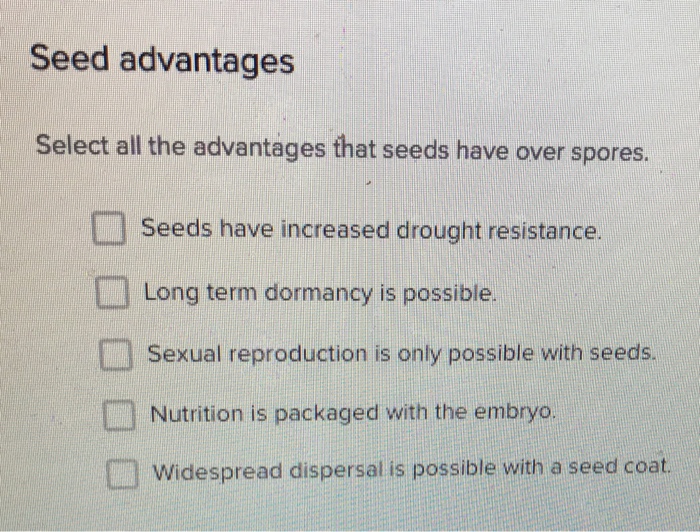



Select All The Advantages That Seeds Have Over Chegg Com
The evolution of seeds allowed plants to decrease their dependency upon water for reproduction Seeds contain an embryo that can remain dormant until conditions are favorable when it grows into a diploid sporophyte Seeds are transported by the wind, water, or by animals to encourage reproduction and reduce competition with the parent plant Key TermsIn this KS2 Science quiz we take a look at plant reproduction This involves the different parts of flowers, pollination, seed dispersal and germination All living organisms reproduce but what exactly is reproduction?Propagation Azaleas can be propagated sexually, from seed, or asexually (vegetatively) from cuttings, layers, grafts or by tissue culture Different seedlings from a cross between two different azaleas may exhibit characteristics of either parent and anything in between While seedlings from a selfpollinated species azalea will tend to
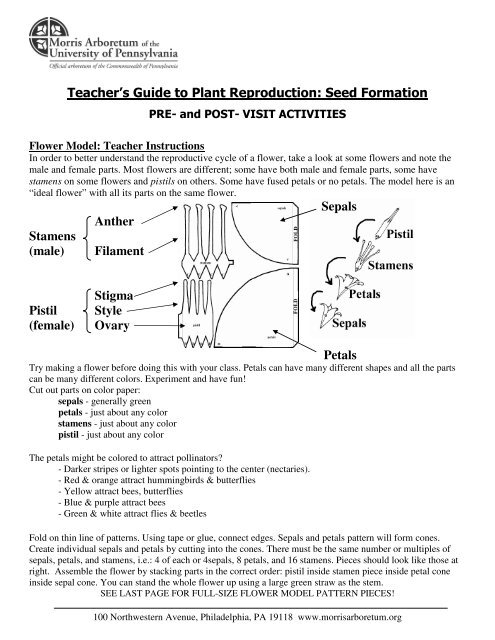



Teacher S Guide To Plant Reproduction Seed Formation Sepals
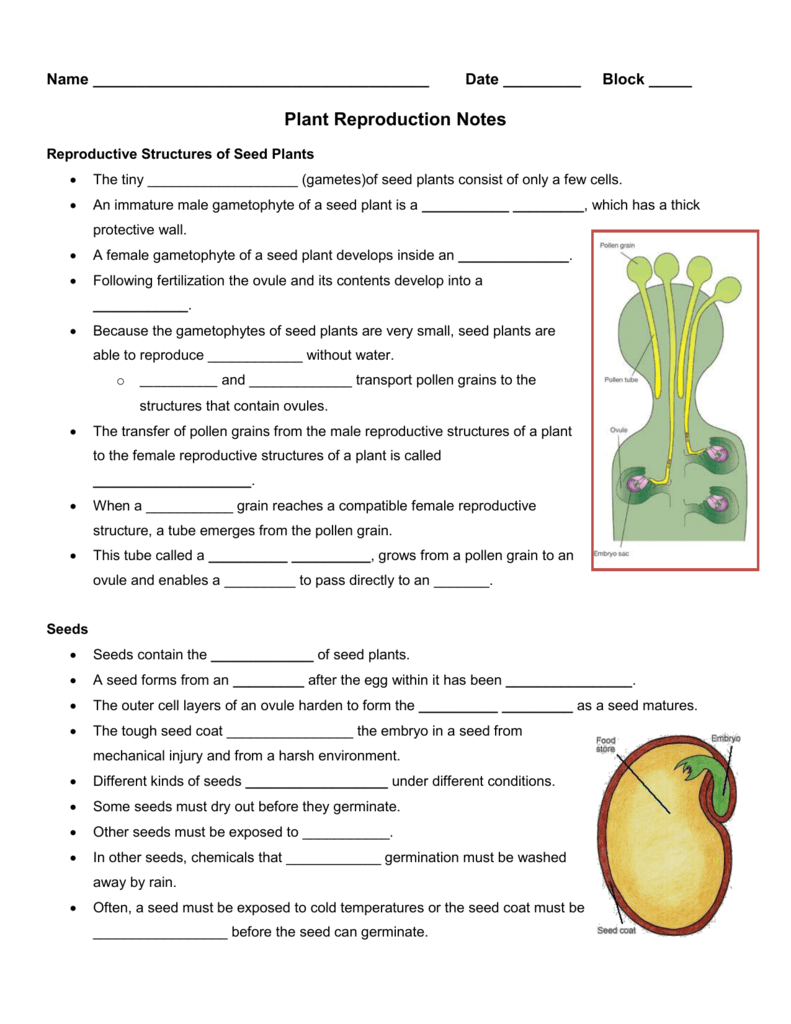



Plant Reproduction Notes Outline
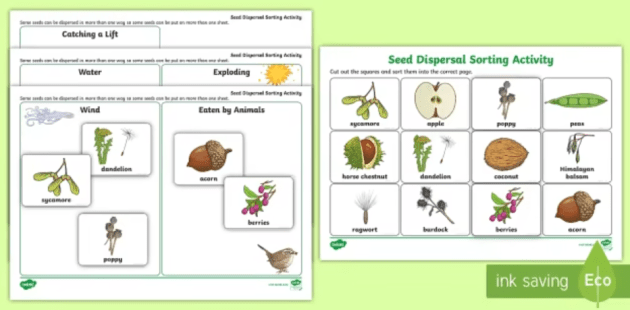
A number of parts of the reproductive process are common to both angiosperms and gymnosperms (1) they produce seeds at maturity;Seed Reproduction * Description/Instructions ; Name_____ For each of the seeds shown state its mechanism for seed dispersal and describe the adaptations that are suited to the mechanism Name of plant Diagram of seed Seed dispersal mechanism Adaptations Lupin mechanical Dries unevenly and splits open with force shooting the seeds outwards Biology IGCSE Plant Reproduction 8 Backberry




Learn Characteristics Of Living Organisms Nutrition Growth Reproduction And Lifespan In 3 Minutes




Vegetative And Seed Reproduction Of Plants Tubers Bulbs And Seeds Isolated On White Background Stock Illustration Download Image Now Istock
Seed And Fruit Formation Seed Dispersal Reproduction is the biological process where a new individual organism is produced by their parents In general, plants reproduce either asexually ie without seed formation or sexually ie with seed formation Professor Koltunow said sexual reproduction naturally separated genetic traits in seeds formed in flowers of the hybrid "The key to preserving the seed yield gains of hybrids from one generation to the next lies with one of the quirkiest aspects of plant reproductive biology 'apomixis' – a naturally occurring asexual seed formation pathway in plants," she saidNote on which specimens to propagate Healthy plants As always when propagating, make sure you've got a healthy ZZ plant There should be no trace of disease or weakness, since propagation will further weaken the plant!



Tomatosphere Tomatosphere The Life Cycle Of A Tomato Plant




Plant Reproduction Illustrated Growth And Development Of Organisms Ngss 6 8 Grade
A seed is a part of a flowering plant involved in reproduction It consists of three major parts the embryo, endosperm, and testa The embryo is produced when male and female elements are combined during reproduction It will eventually grow into a new plantThis quiz will discuss how seeds reproduce and what is needed in order for reproduction to happen Group Science Science QuizzesThe video explains how plants reproduce through seeds It shows how seeds germinate and what are required for germination It also explains the importance of




Seed Plants Classification Seeds Seedless Plants Mosses Ferns Ferns Are Vascular Plants Make Spores Not Seeds Embryo From Sexual Reproduction Ppt Download



The Seed Biology Place Seed Evolution
Seed production by annual weeds is crucially important to their survival It is no less important in perennial species where seed production as a consequence of sexual reproduction is important for the reassortment of genes and creation of new biological variability(3) there is a minute passageway, or micropyle, through the integuments; By contrast, local population dynamics of non‐clonal plants must rely on reproduction by seed Clonality and seed reproduction by seed thus constitute two different strategies for colonizing a site, possibly resulting in a negative correlation between them Still data on correlations between (traits of) seed and clonal reproduction are sparse




3drose Verbena Pink Red And Purple Flowers Vintage Seed Packet Reproduction Towel 15 By 22 Inch Walmart Com Walmart Com



Asexual And Sexual Reproduction In Plants Jennifer C
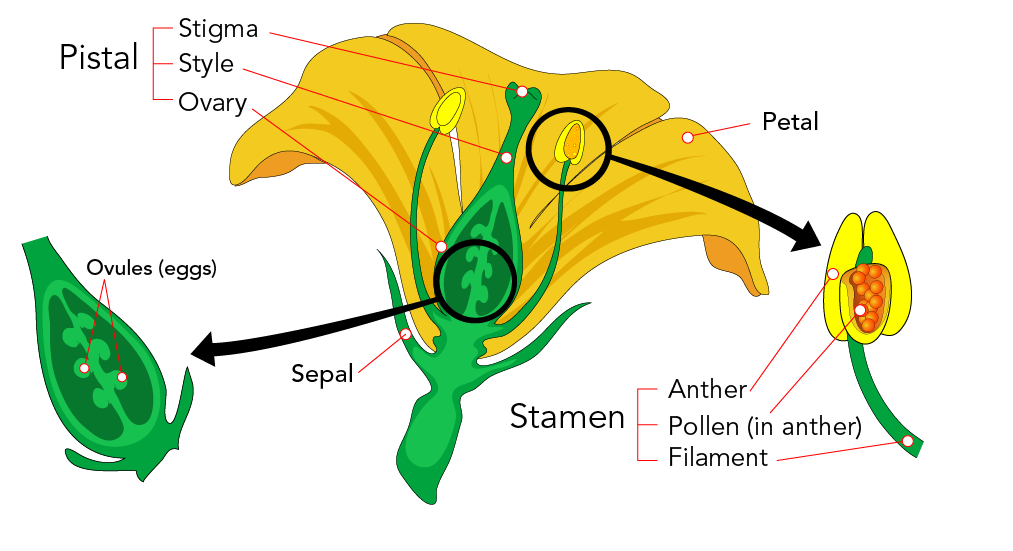
The male parts of the flower (each consists of an anther held up on a filament) Anthers Produce male sex cells (pollen grains) Stigma The top of the female part of the flower which collects
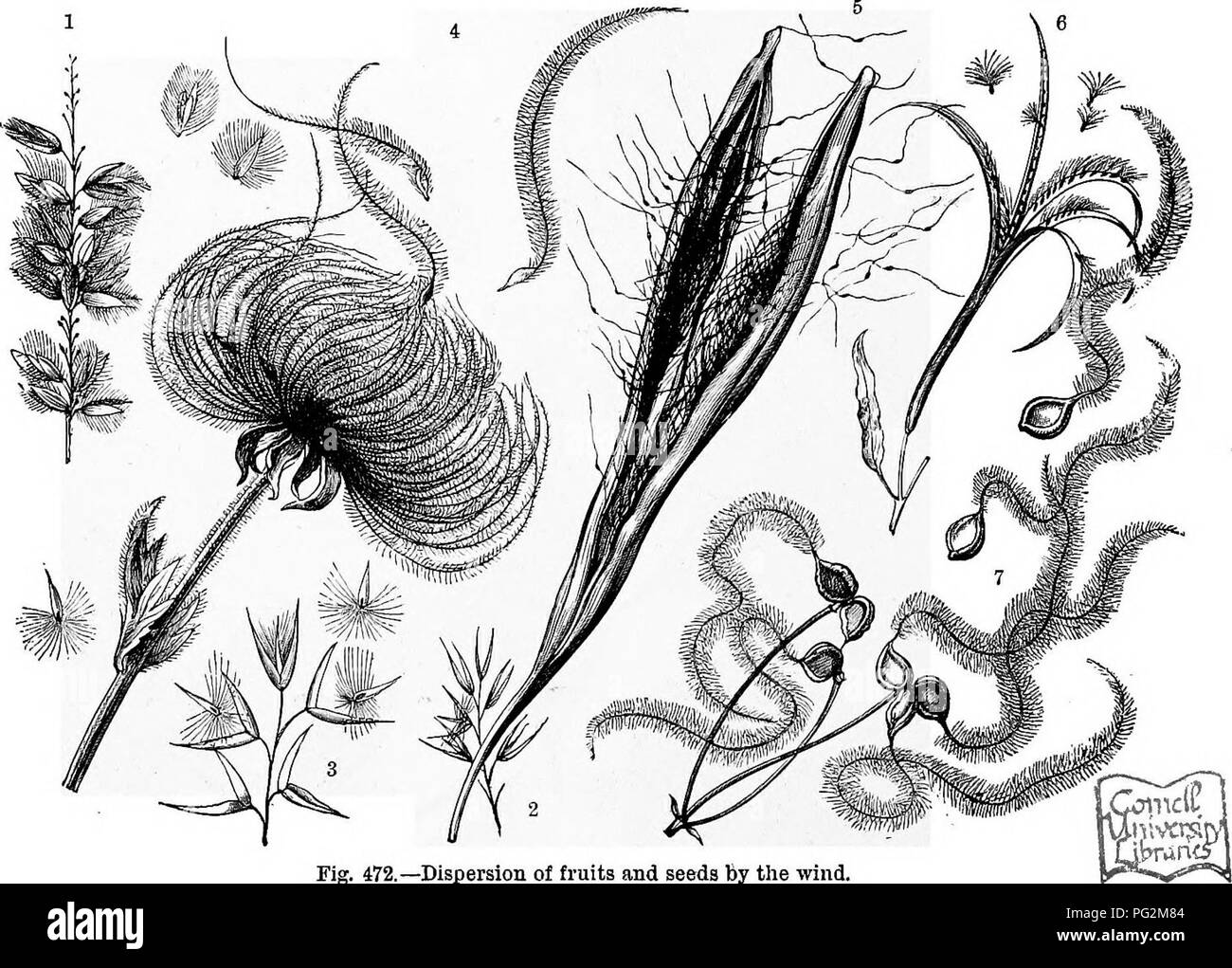




The Natural History Of Plants Their Forms Growth Reproduction And Distribution Botany 858 The Dispersion Of Species By Means Of Fruits And Seeds To Remain Poised In The Air The Hairs



1



British Plants Their Biology And Ecology Plants Plant Ecology Reproduction By Seed 181 The Head Fig 80 Is The Characteristic Inflorescence Of The Dandelion Family The Scabious Thrift Etc The




Plant Reproduction Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock




Plant Reproductive Development And Structure Boundless Biology
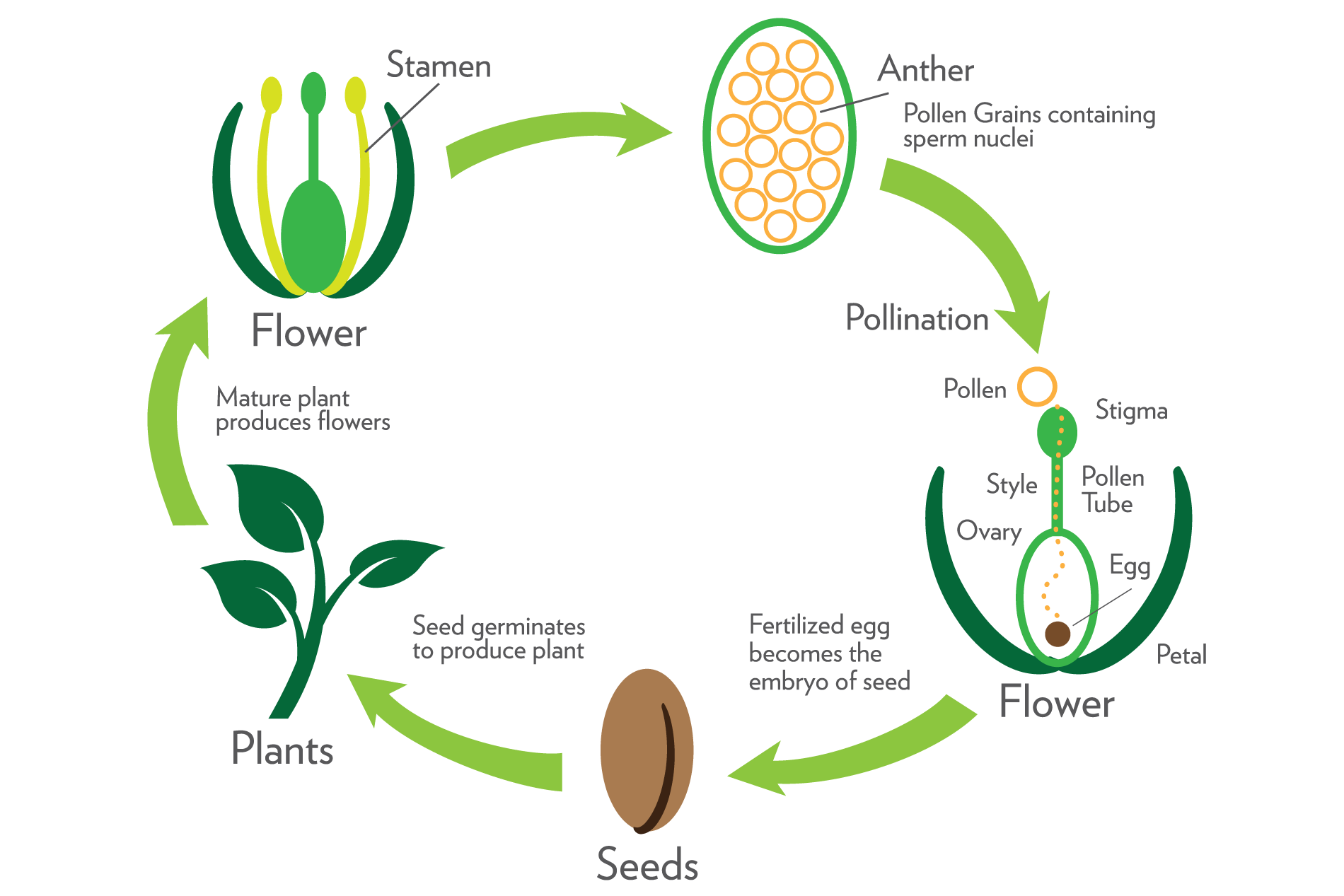



Part 3 Growth Reproduction And Evolution Plant Reproduction Dōterra Essential Oils




Rewiring Plant Reproduction For Higher Seed Yields



The Seed Biology Place Seed Evolution
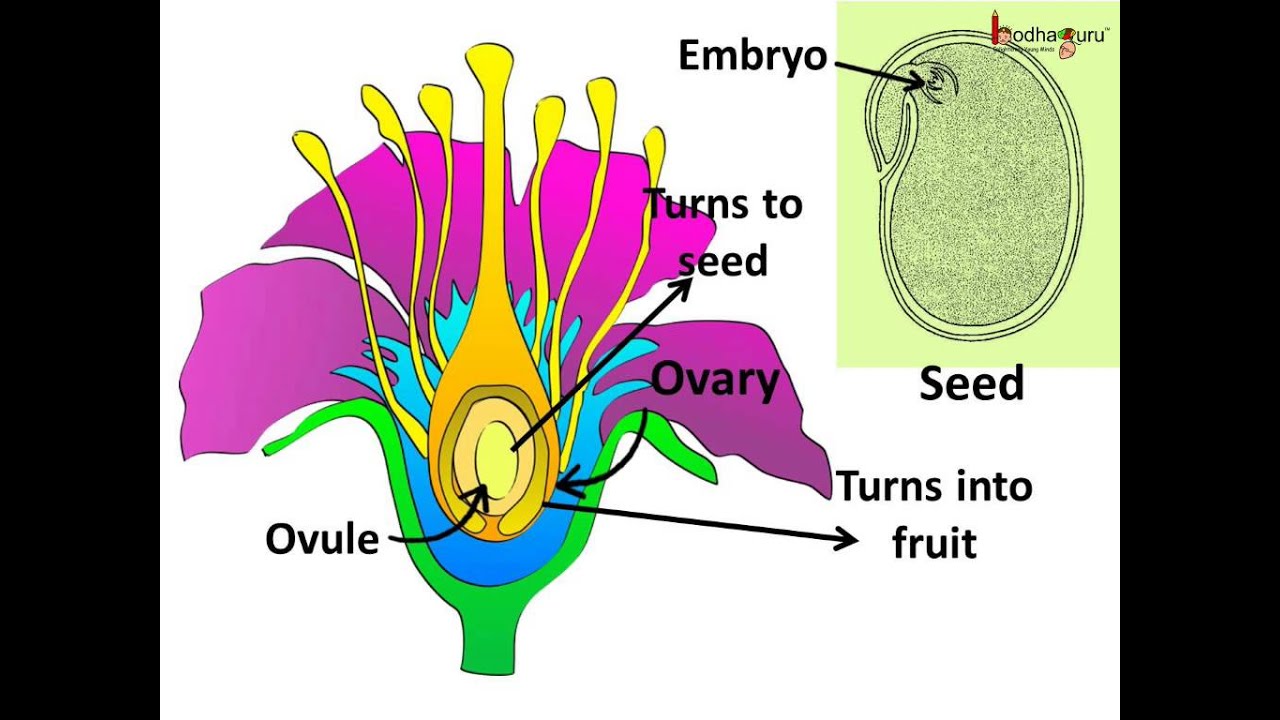



Science Sexual Reproduction In Plants Pollination Fertilization Hindi Youtube




Complex Body Seed Reproduction Flowering Angiosperms Plants Stock Photo Image By C Enigma Art




Amazon Com Vintage Art Print Wall Decor Floral Seed Pack Catalog Cover Art 8 X 10 Reproduction Unframed Posters Prints




Flower Reproduction Illustration Labeled Process Of New Plants Scheme Educational Diagram With Stamen And Pistil Structure And Full Egg Development And Fertilization Stages From Ovule To Seed Royalty Free Cliparts Vectors And




Seed Wikipedia



Plant Reproduction Let S Talk Science




Seed Dispersal Ck 12 Foundation



Chapter 7 Lesson 3 Seed Reproduction Ppt Video Online Download



Plant Reproduction Wordsearch




Plant Reproduction Science Learning Hub




Plant Reproduction




Ovary Botany Definition Structure Britannica



How Do Trees Reproduce Quora



How Do Seed Plants Grow Reproduce




Reproduction Flower Seed Packets Advertising Pictures Set Of 3 Burts Seed Framed Ebay



Ginseng Reproduction




3 Seed Structure Sexual Reproduction In Plants




Reproduction In Lower Higher Plant Part 7 Seed Fruit Development New Syllabus Class 12 Youtube
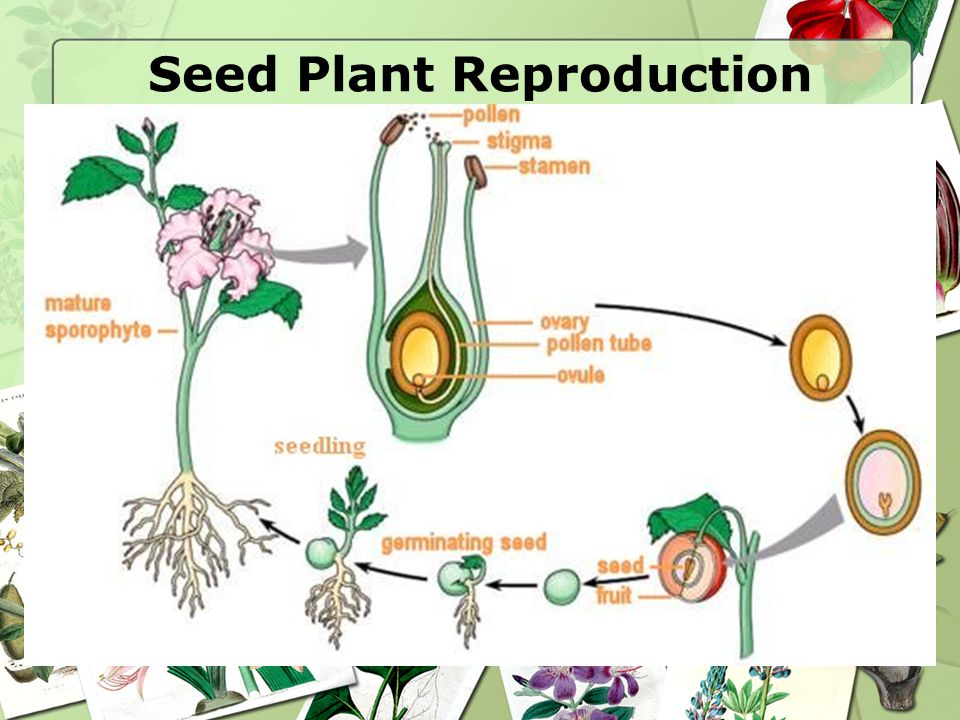



3 2 Notes Plant Reproduction Ppt Download




Seeds And Flowers Plant Reproduction Plants Without Seeds
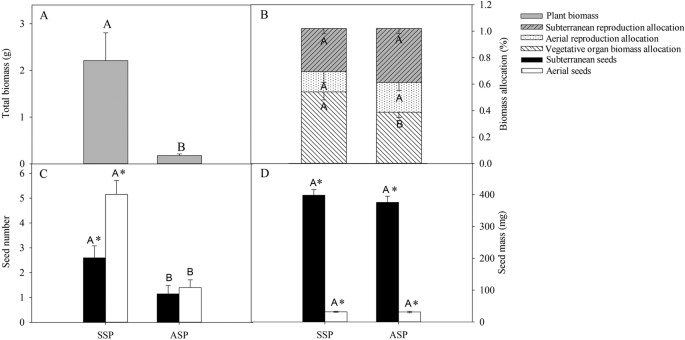



Effect Of Seed Morph And Light Level On Growth And Reproduction Of The Amphicarpic Plant Amphicarpaea Edgeworthii Fabaceae Scientific Reports



Www Cambriansd Org Cms Lib Ca Centricity Domain 390 Ppt as flower reproduction Pdf




Gymnosperms Naked Seed Plants An Overview Of Biodiversity




Plant Reproduction Seed Plants



Flowering Plant Reproduction




Science Plant Reproduction Seed Dispersal Germination English Youtube




Plant Reproduction Seed Plants




Ch 24 Reproduction Of Seed Plants I Reproduction




Reproduction Different Modes Of Plant Reproduction Byju S




Exploring Plant Reproduction And Seed Dispersal Grade 9 Petal Flowers




Seed Form Function Dispersal Germination Britannica
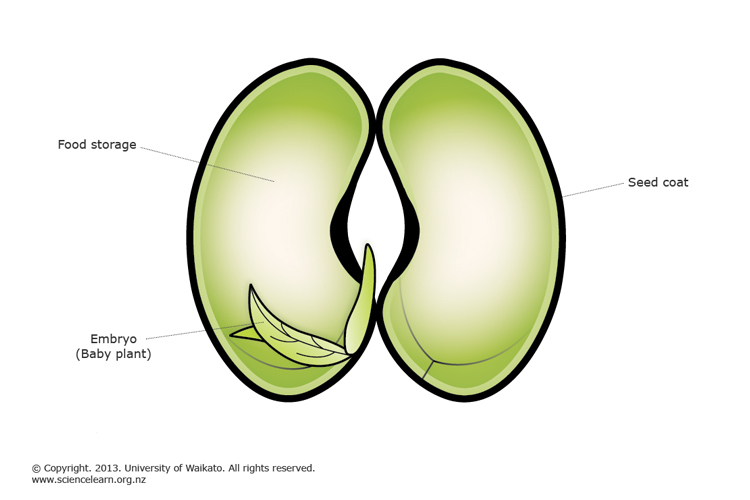



Plant Reproduction Science Learning Hub



1




Complex Body Seed Reproduction Flowering Angiosperms Plants Stock Photo Image By C Enigma Art



Plant Reproduction Biology Junction




Seed Dispersal Interactive Worksheet




Vegetative Reproduction And Sexual Reproduction Modes Of Vegetative Reproduction




Jove Science Education Plant Reproduction



Daffodil Reproduction




Fun Germination Facts For Kids



Reproduction Mucuna Pruriens Velvet Bean Tropical Plant Used To Help Treat Parkinson S Disease
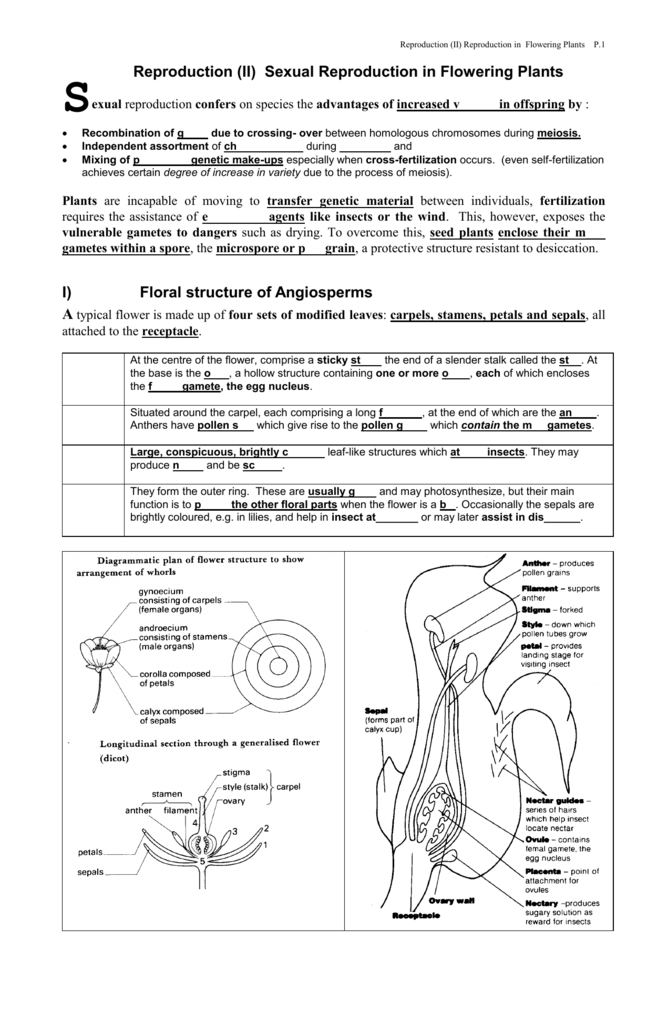



V Advantages And Disadvantages Of Reproduction By Seed




Chapter 24 Reproduction Of Seed Plants By Mihael Maldonado



Asexual And Sexual Reproduction In Plants Jennifer C



What Is Reproduction In Plants Answered Twinkl Teaching Wiki



Plant Reproduction Seed Plants




Overview Of Sexual And Asexual Seed Development In Citrus Major Download Scientific Diagram




Vegetative And Seed Reproduction Of Vegetable Plants Potato Onion Garlic Stock Vector Illustration Of Generative Potato




Seed Dispersal For Kids Reproduction In Plants Youtube Seed Dispersal How To Memorize Things Seeds




Seed Reproduction And Pollination Anson And Wayne By Anson Sieu




Seed Reproduction Chapter 7 Section 3 Importance Of Seeds Pollen Fruits And Vegetables That We Eat Come From Seed Plants All Flowers Are Produced Pptx Powerpoint




Complex Body Seed Image Photo Free Trial Bigstock
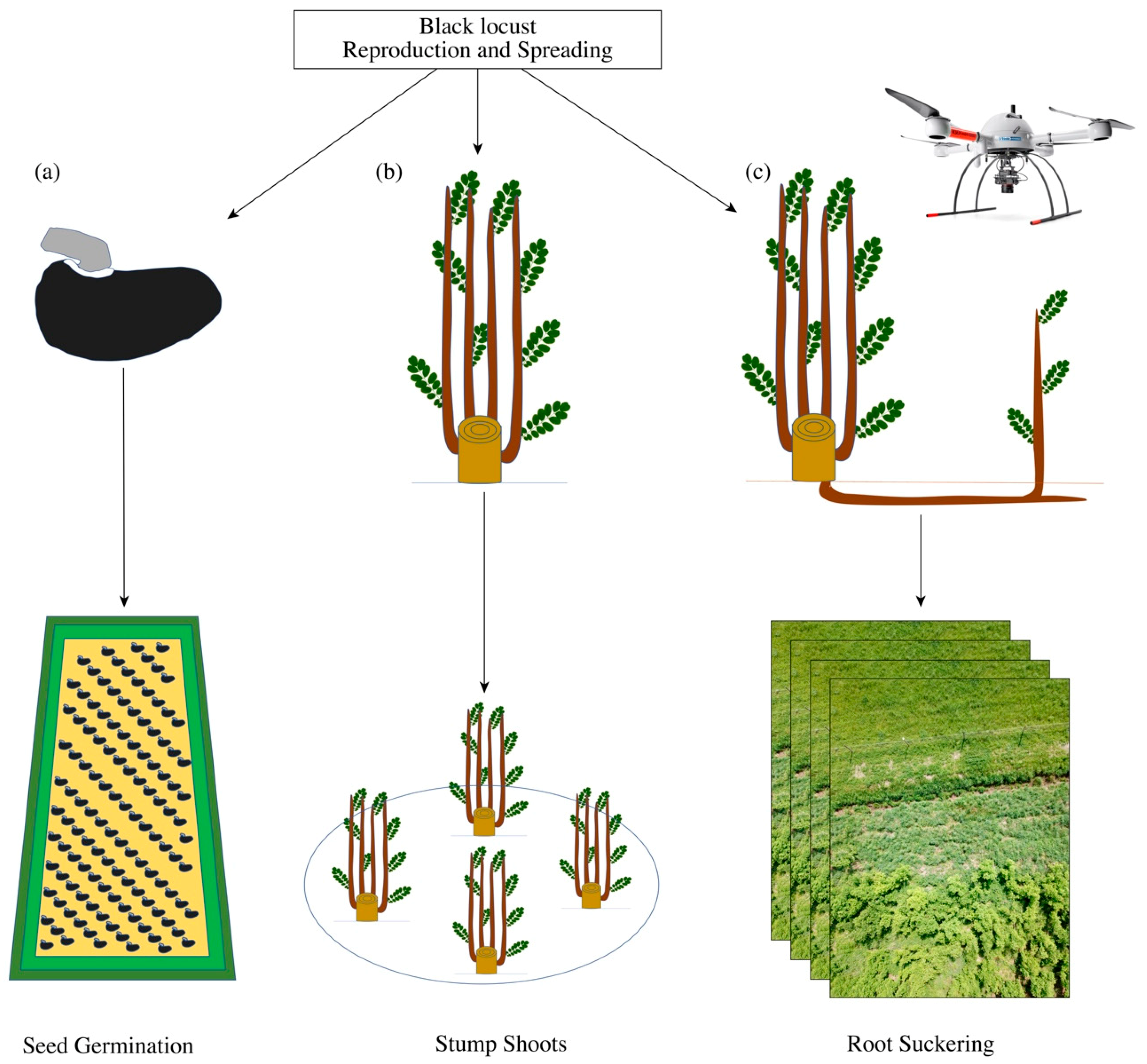



Forests Free Full Text Robinia Pseudoacacia L In Short Rotation Coppice Seed And Stump Shoot Reproduction As Well As Uas Based Spreading Analysis



Plant Reproduction Seeds And Spores Cut And Paste Activity By King Virtue




Class 5th Science Reproduction In Plants Chapter 1 Youtube




Ppt Seed Plant Reproduction Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Growing Plant Stages Color Line Icon The Seed Germination Growth Reproduction Pollination And Seed Spreading Pictogram For Web Page Mobile App Promo Editable Stroke Stock Illustration Download Image Now Istock



Growing Plant Stages Black Glyph Icon The Seed Germination Growth Reproduction Pollination And Seed Spreading Pictogram For Stock Illustration Illustration Of Ground Concept




Where In The Venn Diagram Would Play The Term Seed Seed When Describing Plant Reproduction Brainly Com




Botany Plant Reproduction Laboratory Seed Wikibooks Open Books For An Open World




Ppt Chapter 24 Reproduction Of Seed Plants Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Reproduction System Reproduction Systems In Plants Seed Propagated
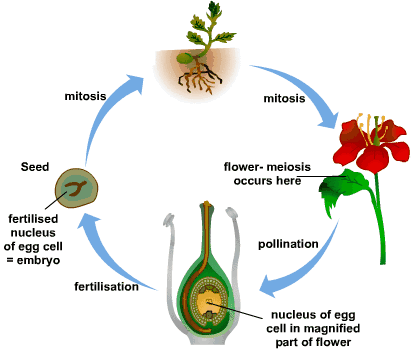



Mcq On Plant Reproduction By Biology Experts Notes Medium



Reproduction In Flowering Plants Presentation Biology
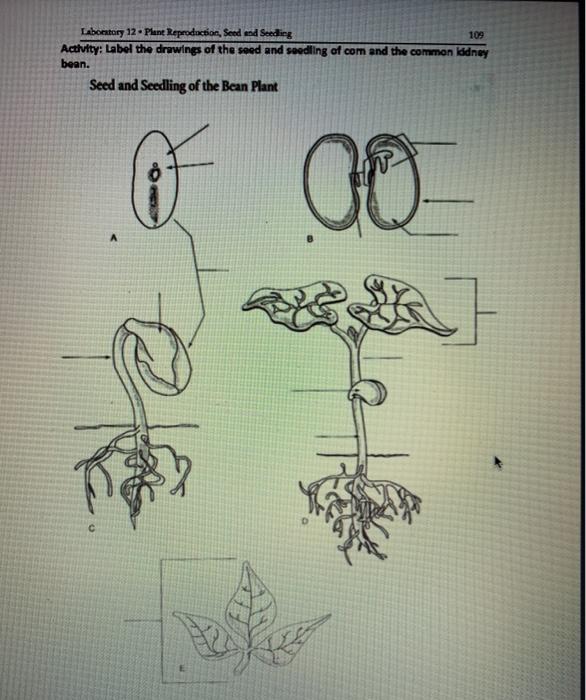



Solved Laboratory 12 Plant Reproduction Seed End Seedin Chegg Com



B2 Sexual Reproduction In Plants Lydia G Narain



1




Fun Germination Facts For Kids



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿